Recently I found myself working on a cryptography project. Being a little rusty on the basics, I decided to take a class to refresh and relearn cryptography. So here are some of my notes for the beginners.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method to exchange information so that only the parties sending and receiving the message can read and process it.
One of cryptography’s significant applications is the security of messages being passed between two parties.
There are two types of crypto-systems:
- Symmetric Cryptosystem
- Asymmetric Cryptosystem
But before we jump into these, let’s define a few terms used in the crypto universe:
- Plain text is the text that is readable and processable by everyone.
- Encryption is the process by which you encode a message, allowing only authorized parties, such as a sender or a receiver, to read and understand the message.
- Cipher Text is the result of the encryption. It is the encoded information which only authorized parties can read and process.
- Key is the sequence that encodes plain text to cipher text and vice-versa.
- Decryption is the conversion of information from cipher text back to plain text.
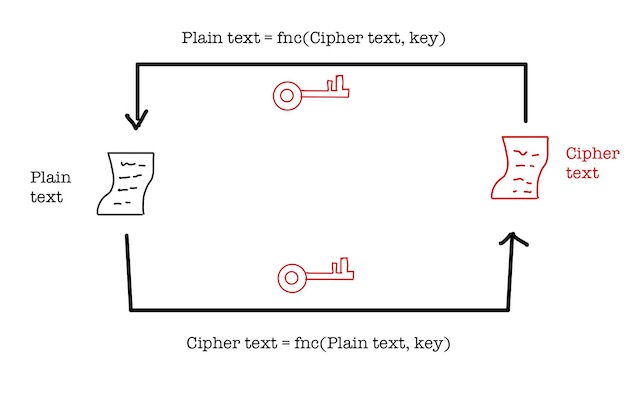
Symmetric Cryptosystem
This type of encryption is also called a private key cryptosystem.
This type of cryptosystem uses a single key for encryption and decryption of the data.
For example, Alice wants to send Bob a gift. Alice locks the box with a private key and sends it to Bob. Bob opens the box with the same private key.
An important algorithm for this type of system is Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Problems with Symmetric Cryptosystem
Sharing the private key is complex. In the case of Alice and Bob, if you look closely, you’ll see that Alice locks the box with a private key. Unless Bob has the same key to open the box, he won’t be able to access the box’s contents. Above, we assumed that Bob had the key to open the box, but if Alice wants to share the key with Bob, she needs to figure out some creative ways. And there is always a chance that a malicious third party might steal the key during the exchange.
There is no authentication on the symmetric encryption. Again let’s look at the example of Alice and Bob. Alice sends the package to the wrong address, and instead of Bob, John receives the packet. Coincidently, John has the same key. Even though the box was meant for Bob, John can access all the contents of the box.
Symmetric Encryption does not scale well. If Alice wants to send the packages to 5 different people securely, she must ensure that she has five keys. Then she needs to ensure those five people have their keys. That makes ten keys total. What if Alice wants to send packages to 100 or 1000, or 10,000 people. You can see how it will quickly become impossible to manage.
The solution to these problems is Asymmetric Crypto Systems
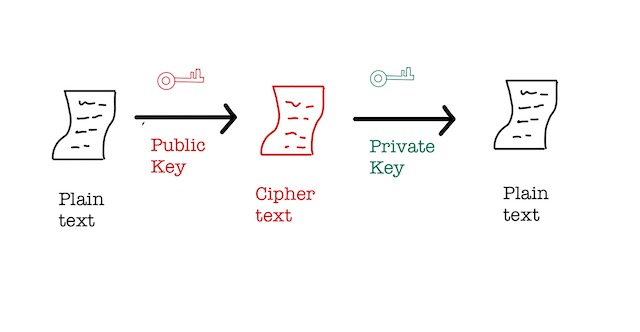
Asymmetric Cryptosystem
These are also called public key cryptosystems. In a symmetric system, there is only one key; in Asymmetric systems, there are two public and private keys.
Public Key transforms plain text to encoded cipher text. This key is shared with every participant in the network.
Private Key converts cipher text back to the readable format of plain text. As the name suggests, this is not shared in the network.
Let’s go back to Alice and Bob. In this type of cryptosystem, when Alice sends a package to Bob, she locks it with Bob’s public key, which only Bob can unlock using his private key.
An important algorithm for this type of system is - Elliptical Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Advantages of Asymmetric Encryption
The private Key doesn’t need to be exchanged. Bob and Alice have their own public and private keys now. The private keys don’t need to be shared, so the chances that someone else will have the same private key or the private key will fall into the hands of a malicious third party are eliminated.
It is more scalable. Now that everyone has their private keys, Alice is no longer responsible for managing the copy of everyone’s private keys.
Summary
These were the basics of cryptography. Let’s quickly summarize what we discussed above.
- Cryptography is a method to exchange information privately and securely.
- There are two types of CryptoSystems -
- Symmetric Encryption, which uses a single private key to encrypt and decrypt the information
- Asymmetric Encryption, which uses two keys. The public key encrypts the information to cipher text, and the related private key decrypts the information into plain text.